 | Comparison H.fagi / H.genava / H.alcyone | |||
 | Comparison H.fagi / H.genava / H.alcyone | |||
 back to H.fagi page back to H.fagi page |  back to H.genava page back to H.genava page |  back to H.alcyone page back to H.alcyone page | ||
| The main criterions for separating these three species are shown on this page, according to the scientific publication mentioned below (1). For a reliable identification, it is necessary to consider all the criterions and look at several specimen of the same population, as some individuals of a species may show some criterions of the other species. It is also useful to keep in mind that a few Hipparchia fagi can mix with the H.alcyone or H.genava. Bibliography : (1) Confirmation de la dualité du "Petit Sylvandre" diagnostiquée par Leraut (1990). 2ème partie : comparaison des critères alaires et des genitalia d'Hipparchia alcyone et d'Hipparchia genava - D.Jutzeler & G.Volpe - Linneana Belgica, Pars XX, n°5, mars 2006 | ||||
| Hipparchia fagi male | Hipparchia genava male | Hipparchia alcyone male | ||
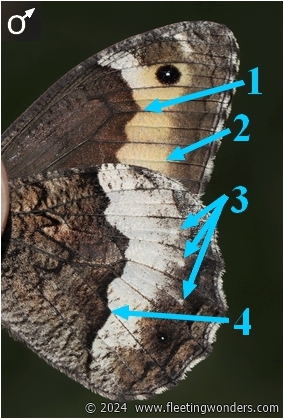 |  | 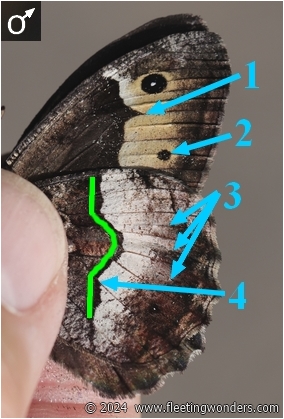 | ||
| 1 : not pointed (obtus angle with mild or no spike) | 1 : not pointed (obtus angle with mild or no spike) | 1: pointed (acute angle) | ||
| 2 : no black spot | 2 : no black spot (a small one in some individuals) | 2 : a black spot in most specimen (a large one usually) | ||
| 3 : white spots well visible in most individuals | 3 : white spots well visible in most individuals | 3 : white spots not clearly visible in most individuals | ||
| 4 : irregularity (along vein 2) of the post-discal dark line (forming an elbow or an unevenness). The dark line looks irregular and often thick. | 4 : irregularity (along vein 2) of the post-discal dark line (forming an elbow or an unevenness). The dark line looks irregular. | 4 : no irregularity along vein 2 (or a small unevenness) The dark line forms an even Omega letter | ||
 |  |  | ||
| 5 : the clear band is wide | 5 : the clear band is narrow | 5 : the clear band is narrow | ||
| 6 : no black spot in most specimen (a weak one in a few individuals) | 6 : no black spot in most specimen (a weak one in a few individuals) | 6 : a black spot in most specimen (a large one usually) | ||
 |  |  | ||
| Genitalia : the number of the small black sticks usually ranges from 3 to 4 in H.fagi. They look pointed. | Genitalia : the number of the small black sticks usually ranges from 8 to 12 in H.genava. | Genitalia : the number of the small black sticks usually ranges from 15 to 30 in H.alcyone. | ||
| Nota Bene : except in H.fagi, the sticks are not always easy to count as some long and brown scales can mix with the black sticks or even hide them. The thickness of the sticks can vary a lot within H.genava and H.alcyone and is not a clue for separating them, as well as their lenght. The checking of the genitalia has to be done gently in order not to damage the living insect which will then fly away quickly when released. | ||||
| Hipparchia fagi female | Hipparchia genava female | Hipparchia alcyone female | ||
 |  |  | ||
| 3 : no black spot | 3 : often no black spot (a small one in some individuals) | 3 : a black spot in all specimen (a large one usually) | ||
| 4 : the post-discal clear band is completely filled with fine black marbling. The background colour can be white or cream | 4 : the post-discal clear band is mildly filled with fine black marbling | 4 : the post-discal clear band is filled with fine orange marbling | ||
| 5 : the post-discal line is thick | ||||
 |  |  | ||
| 1 : a black spot in most specimen | 1 : a black spot in most specimen | 1 : a black spot in all specimen (usually large) | ||
| 2 : the bright band is wide | 2 : the bright band is narrow (wide in some individuals) | 2 : the bright band is narrow | ||